We continue our blog series on the Email Security Protocols, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, explaining how they work together to enhance email security.
****
For any business, securing email communication is a top priority, especially in light of the rise in mail fraud, spam, spoofing, and phishing attacks. DomainKeys Identified Mail, or DKIM, is a powerful, industry-standard protocol for securing email transmissions. We delve into the underpinnings of DKIM, how it works, and why it’s crucial for protecting your email communications.
What is DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)?
DKIM verifies the authenticity of an email’s origin and its integrity during transit. It combats email spoofing, commonly used in phishing and other spam, that involves an attacker forging the header of an email to make it appear as if it was sent by someone else, often a trusted source. DKIM was developed to help email servers verify that the domain’s administrators indeed authorized the mail coming from a domain and that it has not been tampered with during transit.
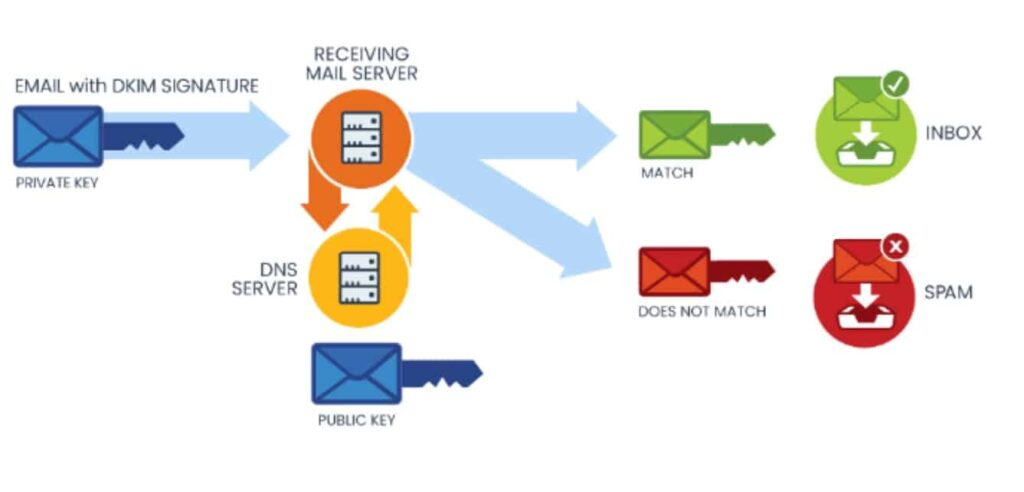
How It Works
DKIM works by adding a digital signature to outgoing emails using cryptographic techniques. This signature, which is unique to each sender, is stored in the sender’s domain’s DNS records. When the recipient server receives the email, it verifies the signature using the public key stored in the sender’s DNS records. If the signature is valid, it confirms that the email has not been tampered with during transmission and that it originated from the claimed domain.
The crux of DKIM lies in its use of public-key cryptography, which involves a pair of mathematically related keys: a private key to sign the email and a corresponding public key to verify the signature. This public key is published in the DNS record of the sender’s domain, allowing the recipient’s server to fetch it for verification. If the verification process is successful, it provides a certain level of trust that the claimed domain indeed sent the email and hasn’t been altered along the way.
The Importance of DKIM
DKIM provides an added level of validation and trust in the chaotic world of emails. It serves two main purposes:
- Prevents Email Spoofing: By signing the email with a private key, DKIM ensures that the email is genuinely from the sender it claims to be from. This technique helps prevent spoofing, where attackers send emails pretending to be someone else.
- Preserves Message Integrity: The signature also includes information about the content of the email. If any part of the email body or certain parts of the header are altered during transit, the DKIM signature will not validate correctly at the recipient’s end, indicating tampering.
Is DKIM Enough?
While DKIM is a powerful tool, it’s not a silver bullet for email security. It is only part of a larger suite of email authentication protocols, including SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance). SPF prevents spammers from sending emails on behalf of your domain, while DMARC builds upon both SPF and DKIM, providing a policy framework that recipients can use to handle authentication failures. Stay tuned for our upcoming posts, where we’ll dive deeper into DMARC and how these complementary technologies work together.
Concerned about email security? We can help!
With phishing, whaling, and spoofing on the rise, are you looking for experts who can protect your business? Vernovis can help! Learn more about our Consulting and Advisory Services, designed to help your technology infrastructure is humming and scalable… securely.






